
Benoit Wtterwulghe
IT Consulting
In today's digital landscape, businesses face unprecedented challenges when it comes to safeguarding their sensitive information. The threat landscape is evolving rapidly, and regulatory requirements are becoming increasingly stringent.
At BDO, we understand the critical importance of protecting your organisation's digital assets and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Our team of highly skilled professionals specialises in providing comprehensive ICT Security & Compliance solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of your business. We provide you with expertise and guidance to support you in your compliance journey by helping you navigate the regulatory challenge through:
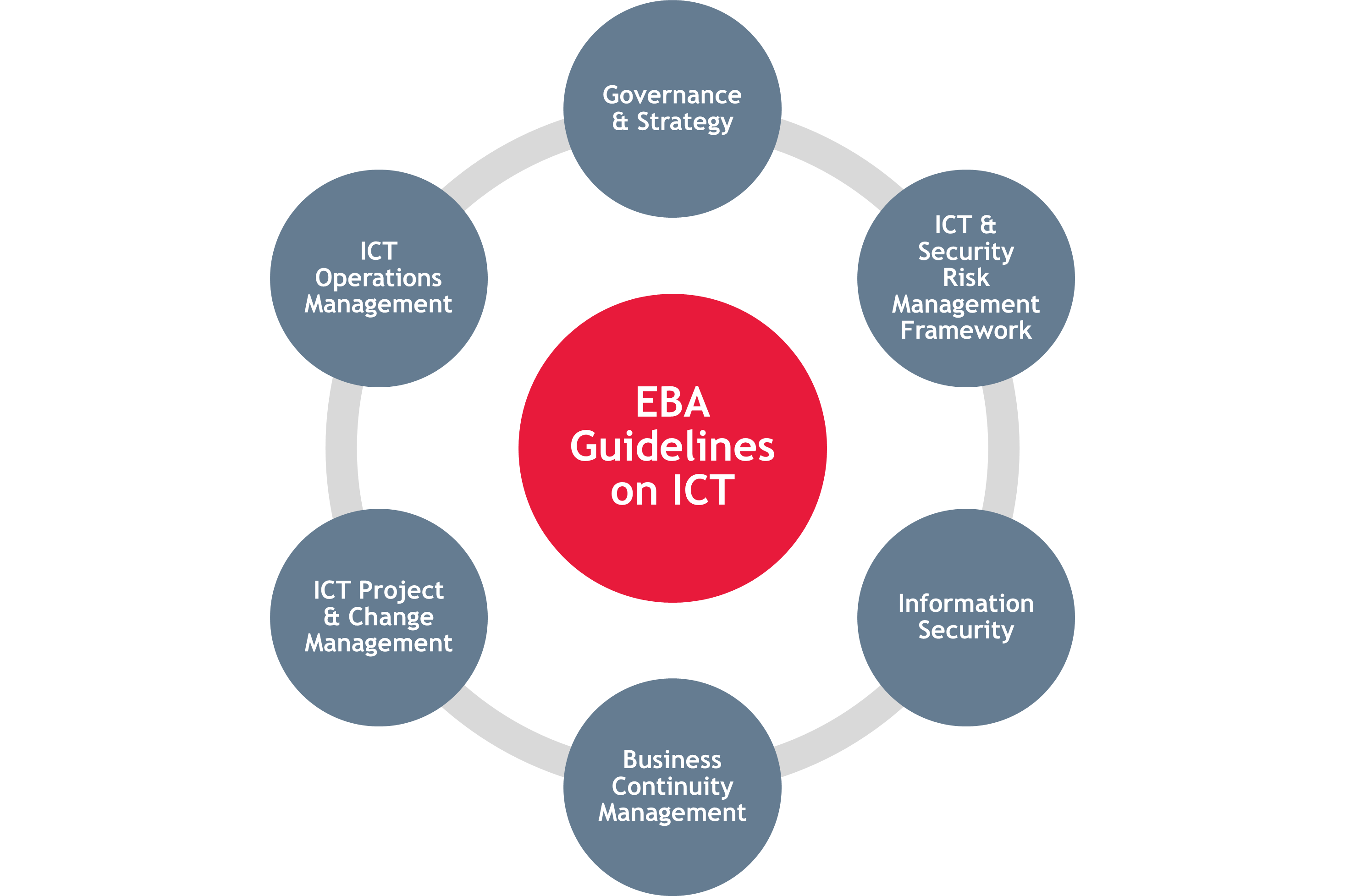
IT Governance Circular CSSF 20/750 (as amended by Circular CSSF 22/828) Requirements regarding information and communication technology (ICT) and security risk management:

IT Outsourcing
Entities in scope:
AlFMs, CSDs, credit institutions, DRSP, E-money institution, SICAR, investment firms, Management Companies – Chapter 15, Payment institution, Pension Funds, Securitisation undertakings, SIF, Specialised PFS, Support PFS, UCI, UCITS
The main purpose of this circular is to:
Entities in scope:
Insurance & Reinsurance Companies
In the context of circular letter 20/13, in which the Commissariat aux Assurances informed the insurance and reinsurance companies subject to its supervision that it would fully apply the "Guidance on outsourcing to cloud service providers", circular 21/15 is intended to take up a set of guidelines and to integrate certain additional CAA requirements.
Entities in scope:
Insurance & Reinsurance Companies
Luxembourg insurance and reinsurance companies are required to inform the CAA of their intention to outsource important operational activities or functions or compliance, internal audit or actuarial functions (deemed critical), as well as of any subsequent significant developments concerning these functions or activities. The purpose of this circular is to specify the CAA's requirements regarding the outsourcing of important or critical operational activities or functions, and their notification to the CAA.
2. EU Regulations

These goals are achieved through requirements outlined in five primary pillars:
ICT risk management, ICT related incident management, including payment-related incidents, digital operational resilience testing, management of ICT third-party risks and oversight of critical ICT third-party service providers, and information and intelligence sharing.
NIS 2, or the Network and Information Security Directive 2, is a European Union legislative framework aimed at enhancing cybersecurity across the EU. It builds upon the original NIS Directive (2016) and seeks to address emerging cyber threats and improve the resilience of critical infrastructure. NIS 2 expands the scope to include more sectors, such as healthcare, digital infrastructure, and public administration, while imposing stricter security and reporting requirements. It aims to foster greater cooperation between EU member states and establish more consistent and effective cybersecurity measures across the union. The directive mandates that companies implement robust security measures, report incidents promptly, and undergo regular assessments to ensure compliance.
Its main goals are:
PSD2 is a game-changer in the financial sector, aimed at promoting competition, innovation, and enhancing consumer protection. It requires banks and other financial institutions to open up their payment infrastructure to third-party providers (TPPs) through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). This means that customers can now securely share their financial data with authorised TPPs to access a range of innovative services, such as payment initiation, account aggregation, and personalised financial advice.
The Payment Services Directive 3 (PSD3) and the Payment Services Regulation (PSR) are upcoming legislative frameworks by the European Union aimed at enhancing the payment services landscape.
The primary objectives include:

Benoit Wtterwulghe